The Evolution of Computers
The Evolution of Computers: A Journey Through Generations
The history of computers is a fascinating tale of innovation and technological advancement. As we trace the evolution of computing, we can identify distinct periods known as “generations.” Each generation represents a significant leap forward in terms of size, speed, power consumption, and capabilities.
First Generation (1940-1956): Vacuum Tubes
The first generation of computers relied on bulky vacuum tubes as their primary electronic components. These tubes were large, consumed a lot of power, and generated significant heat. Machines like ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) and UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) were pioneers of this era. They were primarily used for scientific and military calculations and were incredibly expensive and difficult to operate.

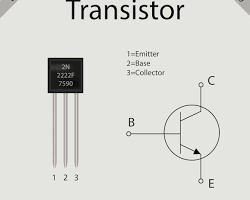
Second Generation (1956-1963): Transistors
The second generation saw the introduction of transistors, which were smaller, more reliable, and consumed less power than vacuum tubes. Transistors revolutionized computer technology, leading to smaller, faster, and more affordable machines. Early transistor-based computers like the IBM 1401 and the CDC 6600 were significant advancements.
Third Generation (1964-1971): Integrated Circuits
The third generation marked a major breakthrough with the development of integrated circuits (ICs). ICs packed multiple transistors onto a single silicon chip, further reducing size and increasing efficiency. This led to the creation of minicomputers, which were smaller and more affordable than their predecessors. Examples of third-generation computers include the IBM 360 and the PDP-8.
Fourth Generation (1971-Present): Microprocessors
The fourth generation witnessed the emergence of microprocessors, single-chip computers that could perform all the functions of a computer. This innovation paved the way for the development of personal computers (PCs). Intel’s 4004 microprocessor was a landmark achievement, and it soon became the foundation for the PC revolution.

Fifth Generation (Present and Beyond): Artificial Intelligence
The fifth generation of computers is still evolving and focuses on artificial intelligence (AI). Researchers are working on developing machines capable of understanding natural language, reasoning, and learning from experience. While significant progress has been made, achieving true AI remains a challenging goal.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking developments in the field of computing. The future of computers promises to be exciting and full of possibilities.